Find All Solutions of Sinx Secx
Ways of solving trigonometric equations with detailed solutions are presented along with graphical interpretation.
Free Practice for SAT, ACT
and Compass Math tests
-
Question
Find all solutions of the equation
sin(x) = 1 / 2 in the interval [0 , 2π) and explain the solutions graphically using a unit circle and the graph of sin (x) - 1/2 in a rectangular coordinate system of axes.Solution
sin(x) is positive in quadrant I and II and therefore the given equation has two solutions.
In quadrant I, the solution to sin(x) = 1 / 2 is x = π / 6. (green in unit circle)
In quadrant II, and by symmetry of the unit circle, the solution to sin(x) = 1 / 2 is x = π - π / 6 = 5π/6 (brown in unit circle)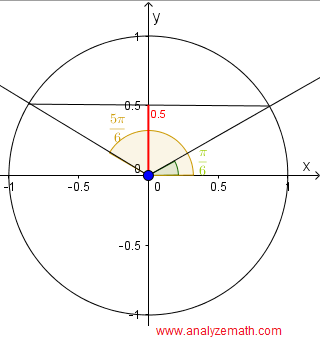


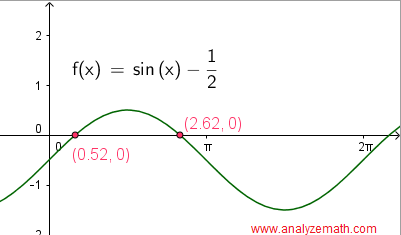
The graphical solutions of the equation sin(x) = 1 / 2 are obtained by first writing the equation with right side equal to zero sin(x) - 1 / 2 = 0. Then graph the left side of the equation and the solutions of the equation are the x - intercepts of the graph of f(x) = sin(x) - 1 / 2 as shown below. It is easy to check that the two x intercepts in the graph below are close to the the analytical solutions found above:π / 6 and 5π/6.


-
Question
Find all solutions of the equation
sin(x) + cos(x) = 0 in the interval [0 , 2π) and explain the solutions graphically using the unit circle and the graph of sin (x) + cos(x) in a rectangular coordinate system.Solution
The equation may be written as: sin(x) = -cos(x).
Divide both sides of the equation by cos(x): sin(x)/ cos(x) = -1
Use the identity tan(x) = sin(x)/cos(x) to rewrite the equation as: tan(x) = - 1
Solve the equation tan(x) = - 1
tan(x) is negative in quadrant II and IV
Solution in quadrant II: x = 3π/4
By symmetry of the unit circle, the solution in quadrant IV is given by: 3π/4 + π = 7π / 4


The graphical solutions may be approximated by the x intercepts of the graph of g(x) = sin(x) + cos(x). We can easily check that the two solutions found above 3π/4 and 7π/4 are close to the x intercepts of the graph shown below.



-
Question
Find all solutions of the equation:
sin(πx / 2)cos(π/3) - cos(πx / 2)sin(π/3) = 0
and check graphically the first few positive solutions.Solution
We first use the formula sin(A - B) = sin A cos B - cos A sin B
to write : sin(πx / 2)cos(π/3) - cos(πx / 2)sin(π/3) = sin(πx / 2 - π/3)
rewrite the given equation as follows: sin(πx / 2 - π/3) = 0
Solve the above equation to obtain: πx / 2 - π/3 = k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...
Simplify and rewrite the solution as: x = 2 k + 2/3 where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...


The first 3 positive solutions are: 2/3 , 8/3 and 14/3 corresponding to k =0, 1 and 2. These values are close to the x intercepts of the graph of f(x) = sin(πx / 2)cos(π/3) - cos(πx / 2)sin(π/3) shown above.
-
Question
Find all solutions of the equations: 2 sin2(x) + cos (x) = 1.
and check graphically the first few positive solutions.Solution
We first use the identity: sin2(x) = 1 - cos2(x)
to rewrite the equation as: 2(1 - cos2(x)) + cos (x) = 1
group like terms and write equation with right side equal to zero: -2 cos2(x) + cos (x) +1 = 0
Let u = cos (x) and rewrite the equation as: -2 u2 + u +1 = 0
Solve for u: u = 1 and u = - 1 / 2
First group of solutions: Solve u = 1 for x: u = cos (x) = 1 : x1 = 2 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...
Solve u = -1 / 2 for x:
cos(x) is negative in quadrant II and III, hence u = cos (x) = - 1/2 has two more groups of solutions given by
Second group of solutions: x2 = 2π/3 + 2 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...
Third group of solutions: x3 = 4π/3 + 2 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...


The first 3 positive solutions are obtained by setting k = 0 in all three groups of solutions to obtain: 0, 2π/3 and 4π/3. These values are close to the x intercepts of the graph of g(x) = 2 sin2(x) + cos (x) - 1 shown above.
-
Question
Find all solutions of the equation: 6 cos2(x / 2) - cos (x) = 4.
and check graphically the first few positive solutions.Solution
We first use the identity: cos(x) = 2 cos2(x / 2) - 1
to rewrite the equation as: 6 cos2(x / 2) - (2 cos2(x / 2) - 1 ) = 4
group like terms and write equation with right side equal to zero: 4 cos2(x / 2) = 3
cos(x / 2) = ~+mn~ √3 / 2Solve the first equation cos(x / 2) = √3 / 2
the cosine function is positive in quadrant I and IV hence the two groups of solutions:x / 2 = π / 6 + 2 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ... (quadrant I)
and
x / 2 = 11π / 6 + 2 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ... (quadrant VI)Multiply all terms by 2 to obtain the first two groups of solutions:
x1 = π / 3 + 4 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...
x2 = 11π / 3 + 4 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...Solve the second equation cos(x / 2) = - √3 / 2
The cosine function is negative in quadrant II and III hence the two groups of solutions:x / 2 = 5 π / 6 + 2 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ... (quadrant II)
and
x / 2 = 7 π / 6 + 2 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ... (quadrant III)Multiply all terms by 2 to obtain two more groups two of solutions:
x3 = 5 π / 3 + 4 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...
x4 = 7 π / 3 + 4 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...


The first 4 positive solutions are obtained by setting k = 0 in all four groups of solutions to obtain: π/3 , 5π/3, 7π/3 and 11π/3. These values are close to the x intercepts of the graph of f(x) = 6 cos2(x / 2) - cos (x) - 4 shown above.
-
Question
Solve the equation: tan2 ( x) + 2 sec (x) + 1 = 0.
and check graphically the first few positive solutions.Solution
We first use the identity: tan2(x) = sec2(x) - 1
to rewrite the equation as: sec2(x) - 1 + 2 sec (x) + 1 = 0
group like terms and write equation with right side equal to zero: sec2(x) + 2 sec (x) = 0
Factor: sec (x) (sec (x) + 2) = 0
sec (x) = 0 has no solution.
Solve : sec (x) + 2 = 0
Use sec (x) = 1 / cos (x) to rewrite equation as : cos(x) = - 1 / 2The cosine function is negative in quadrant II and III hence two groups of solutions
x1 = 2π/3 + 2 k π where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...
x2 = 4π/3 + 2 k π; where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ...


The first 2 positive solutions are obtained by setting k = 0 in the two groups of solutions to obtain: 2π/3 and 4π/3. These values are close to the x intercepts of the graph of f(x) = tan2 ( x) + 2 sec (x) + 1 shown above. -
Question
Solve the equation: cos(3x) + sin(2x) = cos(x).Solution
We first use the identities:
cos(3x) = cos3(x) - 3 cos(x)sin2(x)
and
sin(2x) = 2sin(x) cos(x)
to rewrite the given equation as follows: cos3(x) - 3 cos(x)sin2(x) + 2sin(x) cos(x) = cos(x)Rewrite with right hand side equal to zero and factor cos(x)
cos(x) ( cos2(x) - 3 sin2(x) + 2 sin(x) - 1) = 0Use the identity cos2(x) = 1 - sin2(x) to rewrite equation as follows
cos(x) (1 - sin2(x) - 3 sin2(x) + 2 sin(x) - 1) = 0Simplify
cos(x) (- 4 sin2(x) + 2 sin(x) ) = 0Factor
2 sin(x) cos(x) (1 - 2 sin(x)) = 0Set each factor equal to zero and solve.
sin(x) = 0 gives solutions: x1 = kπ
cos(x) = 0 gives solutions: x2 = π/2 + kπ
1 - 2 sin(x) = 0 or sin(x) = 1/2 gives 2 other gropus of solutions.
x3 = π/6 + 2kπ
and
x4 = 5π/6 + 2kπ


The first 6 positive solutions are obtained by setting k = 0 and k = 1 in the first two groups of solutions x1 and x2 to obtain: 0 , π, π/2, 3π/2, and k = 0 in the second and third groups of solutions x3 and x4 to obtain π/6 and 5π/6. These 6 solutions are close to the x intercepts of the graph of f(x) = cos(3x) + sin(2x) - cos(x) shown above.
-
Question
Solve the equation: cos(3x) = cos(2x + π/4).Solution
We use the fact that if cos(A) = cos(B), then A = B + 2kπ or A = - B + 2kπ to write:3 x = 2 x + π/4 + 2kπ
or
3 x = -(2 x + π/4) + 2kπSolve 3 x = 2 x + π/4 + 2kπ Solutions: x1 = π/4 + 2kπ
Solve 3 x = -(2 x + π/4) + 2kπ ,
gives 5x = - π/4 + 2kπ
divide all terms by 5 : x2 = - π/20 + 2kπ / 5
where k = 0 , ~+mn~ 1 , ~+mn~ 2, ... in both groups of solutions


The 6 x intercepts shown in the graph of f(x) = cos(3x) - cos(2x + π/4) below correspond the solutions k = 0 in the first group x1 and k = 0, 1, 2 ,3 and 4 in the second group of solutions x2 = - π/20 + 2kπ / 5.
Find All Solutions of Sinx Secx
Source: https://www.analyzemath.com/high_school_math/grade_12/trigonometry_equations.html